AI innovations in plant breeding: A joint review by ICS-CAAS, CIMMYT, and global research institutions
Nov. 11, 2024
The Institute of Crop Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (ICS-CAAS), in collaboration with the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and Pakistan’s Quaid-i-Azam University, published a comprehensive review titled ″Artificial intelligence in plant breeding.″ This article, which was invited and published online on August 8, 2024, in the renowned journal Trends in Genetics, discusses the emerging trends and future prospects of artificial intelligence (AI) in plant breeding.
AI has demonstrated transformative potential across multiple scientific domains, particularly in plant breeding, where traditional analytical methods often struggle to manage the vast and complex genotype and phenotype data. There are over 1,750 global plant germplasm repositories, housing more than 7 million germplasm resources. However, due to the limitations of current analytical tools, many of these valuable genetic resources remain underutilized. The primary aim of this review is to explore how AI can assist scientists in more efficiently processing these data, thereby advancing precision and efficiency in plant breeding to address global food security challenges.
In this review, the international team systematically analyzes AI applications across several critical stages of the plant breeding process, including data collection and integration, predictive model construction, genetic diversity mining in germplasm collections, and high-throughput phenotyping. Furthermore, the review discusses the potential of AI in optimizing gene-editing systems and predicting the phenotypic impacts of genetic variation. The authors highlight that AI-driven technologies are set to significantly enhance breeding efficiency at every stage and will play a central role in the future development of breeding technologies.
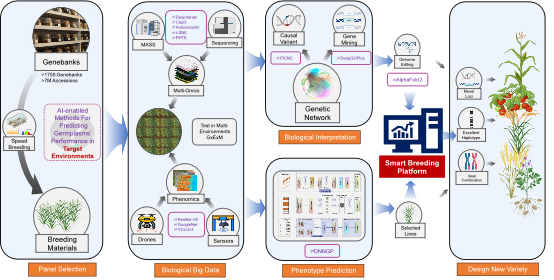
Framework of AI-driven plant breeding
The article's first author is Muhammad Amjad Farooq, a master's student at ICS-CAAS, with Prof. Huihui Li serving as the corresponding author. Substantial collaboration was provided by Prof. Xinhai Li from ICS-CAAS, CIMMYT's principle scientists Drs. Sarah Hearne and Boddupalli Prasanna, and Professor Awais Rasheed from Quaid-i-Azam University. The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Nanfan special project, CAAS, the Key R&D Programs of Hainan Province, and the Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Full article link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2024.07.001
More from AgroNews Change
Change
Subscribe
| Subscribe Email: | * | |
| Name: | ||
| Mobile Number: | ||
Comment
0/1200

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe














